Online Employee & Personnel Management
An online HR database at your fingertips, with important information and
files accessible 24/7 using web-based HRIS / HRMS software.
Employee Management
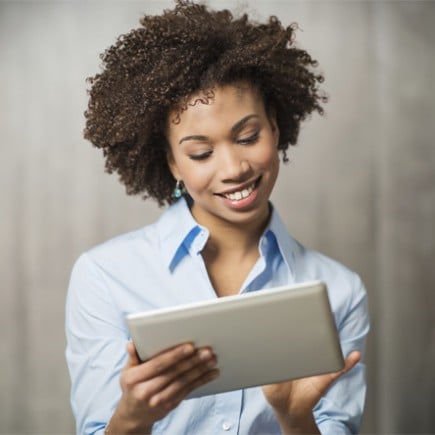


Employee Self-Service Portal
Employees have the ability to view company news, update personal information, request time off,
and clock in/out. Additionally, they can view assigned company property and download shared documents.
Employee Portal
PTO Tracker & Leave Management
Track holiday, sick, vacation, and more. Detailed reporting of accrual balance changes.
Integrated into our time clock, but can be used standalone.
PTO Tracking & Benefits
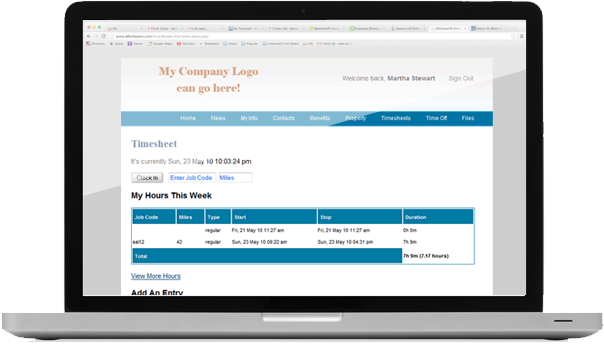
Online Employee Time Clock
Accessible from any computer or smart phone, our time clock is simple and easy to use.
Project management is easy with job codes and custom fields to allow each time entry to be tagged with relevant information.
Employee Time Clock
Cloud Storage of Documents
Store all of your company and employee files in the cloud. Place files in separate virtual folders for compliance.
Online File Storage
Try it free for 30 days. No billing information required.
Testimonials from our clients
As a regional office in charge of 8 different countries we needed to standardize our HR records and reports; we were looking for an HR system that was simple, easy and low cost. We looked at a number of companies, but found that what they offered was mostly time and attendance programs, others were priced out of our budget. Then we had a demonstration from Effortless HR and we were sold!!
This program perfectly fits our needs, gives us flexibility in being able to add additional fields in areas of importance to us and provided great reporting tools. In terms of technical support and service they are outstanding, their tech support, response time and easy solutions are second to none - we would recommend Effortless HR without hesitation.
We think effortlesshr is the future of HR for small and even medium-sized companies. We've been delighted with the service and rapid evolution of its services. Plus, our employees really like getting at all their info online. Actually, given how young our crew of 85 is, they expect it.
We found the perfect solution to our small entity HR needs with Effortless HR. The price is completely affordable, and we have enjoyed watching this dynamic company develop a very useful HR tool for small companies. We have participated with feedback on numerous occasions, and they have responded very quickly to our requests for enhancements. We outsource our payroll and have no need for an expensive full-blown HR package, but we do need to track our employees. It is so convenient to give employees personal access to their benefits, forms and company advisories, and it helps to give managers online access to their departments' employee information rather than having to come to the HR office. This has also answered our need to be able to do mass communication to employees when they evacuate for hurricanes, sometimes an annual occurrence in our area. We lost a lot of data in Hurricane Katrina, but with this online application, we will never have to worry about that, again.